Decoding the S&P 500 can feel like trying to predict the weather – confusing and often inaccurate. Ever wonder why the S&P 500 climbs one day and plummets the next? What's driving these swings, and how can we, as investors, make sense of it all? This article explores Decoding the S&P 500: Key Factors Driving Its Recent Performance, revealing insights into the index's behavior and helping you understand the forces shaping its trajectory.
The recent performance of the S&P 500 hasn't been a simple upward climb. Instead, it's been a rollercoaster ride influenced by a complex interplay of macroeconomic trends, corporate earnings, and investor sentiment. Interest rate decisions by the Federal Reserve, inflation data releases, and geopolitical events have all played a significant role in shaping the index's movement. Additionally, the performance of specific sectors, particularly technology and healthcare, has exerted considerable influence. Changes in these areas can send ripples through the entire index, highlighting the interconnected nature of the market.
To truly understand what's been happening with the S&P 500, we need to delve into several critical areas. First, we'll dissect the macroeconomic landscape , looking at how factors like inflation, interest rates, and economic growth impact the index. Then, we'll analyze corporate earnings , examining how the financial performance of the companies within the S&P 500 contributes to its overall value. Finally, we'll explore the role of investor sentiment , understanding how emotions and expectations can drive market volatility. By exploring these key factors, we can hopefully unravel the mysteries behind the S&P 500's recent ups and downs.
The S&P 500's recent performance hinges on a variety of interconnected factors. Understanding the macroeconomic climate, including inflation and interest rate dynamics, is paramount. Corporate earnings reports offer crucial insights into the financial health of constituent companies. Investor sentiment, often fueled by news and events, adds another layer of complexity. Successfully decoding the S&P 500 requires carefully weighing these elements to anticipate its direction and make informed investment decisions.
The Economic Landscape: Macroeconomic Factors at Play
Interest Rates and Inflation: The Dynamic Duo
Interest rates, set by the Federal Reserve (the Fed), are a major lever influencing the stock market. When the Fed raises interest rates, borrowing becomes more expensive for businesses and consumers. This can lead to slower economic growth, as companies may delay investments and consumers may curb spending. Consequently, lower economic growth can negatively impact corporate earnings, which can then put downward pressure on the S&P 500.
Conversely, when the Fed lowers interest rates, borrowing becomes cheaper, stimulating economic activity. Companies are more likely to invest and expand, and consumers are more likely to spend. This can boost corporate earnings and drive the S&P 500 higher.
Inflation also plays a crucial role. High inflation erodes purchasing power and forces the Fed to consider raising interest rates to cool down the economy. This can create a challenging environment for the stock market. For example, in 2022 and 2023, high inflation forced the Fed to aggressively raise interest rates, contributing to market volatility and a significant decline in the S&P 500.
Example: Look at the period following the 2008 financial crisis. The Fed kept interest rates near zero for years, which helped fuel a long bull market in stocks.
GDP Growth and Unemployment: Gauging Economic Health
Gross Domestic Product (GDP) measures the total value of goods and services produced in a country. A healthy GDP growth rate indicates a strong economy, which typically translates to higher corporate earnings and a rising S&P 500. Conversely, a shrinking GDP suggests an economic slowdown or recession, which can negatively impact corporate earnings and the S&P 500.
Unemployment rates are another key indicator. Low unemployment generally signals a strong economy with plenty of job opportunities. This leads to increased consumer spending and supports corporate earnings. High unemployment, on the other hand, can depress consumer spending and negatively affect corporate profits, leading to a decline in the S&P 500.
Example: During the COVID-19 pandemic in 2020, GDP growth plummeted, and unemployment soared, leading to a sharp decline in the S&P 500. However, massive government stimulus and the Fed's actions helped the economy and the stock market recover relatively quickly.
Geopolitical Events and Global Uncertainties
Geopolitical events, such as wars, political instability, and trade disputes, can inject significant uncertainty into the market. These events can disrupt supply chains, impact global trade, and create volatility in financial markets. Unexpected geopolitical events can lead to sudden sell-offs in the S&P 500 as investors become risk-averse.
Example: The Russian invasion of Ukraine in 2022 caused significant disruptions to global energy markets and triggered a surge in inflation. This geopolitical event contributed to market volatility and negatively impacted the S&P 500.
Corporate Earnings: The Engine of Growth
Earnings Season: A Report Card for Corporate America
Earnings season is when publicly traded companies release their financial results for a particular quarter. These reports provide valuable insights into the financial health of the companies within the S&P 500. If companies consistently beat earnings expectations, it can drive the S&P 500 higher. Conversely, if companies consistently miss earnings expectations, it can put downward pressure on the index.
Analysts closely scrutinize earnings reports for key metrics like revenue growth, profit margins, and earnings per share (EPS). They also pay attention to management's guidance for future performance, as this can provide clues about the company's prospects.
Example: If a company like Apple reports strong earnings and provides optimistic guidance for the future, its stock price is likely to rise. Given Apple's large weighting in the S&P 500, this can contribute to a positive overall performance for the index.
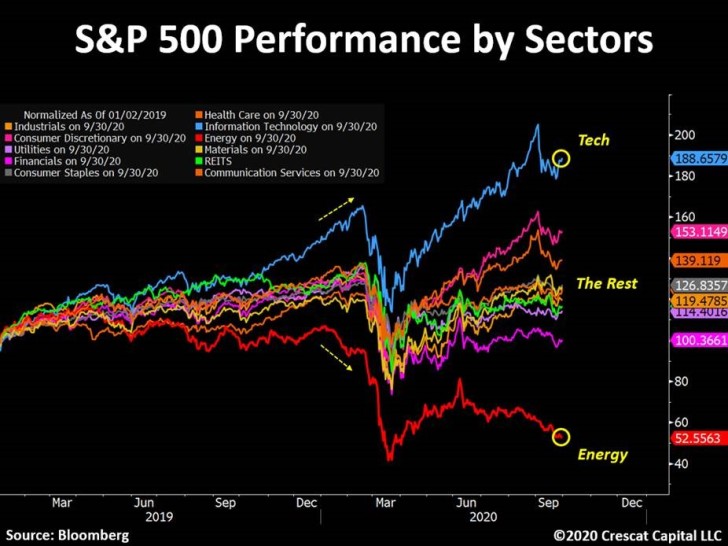
Sector Performance: Identifying the Leaders and Laggards
The S&P 500 is composed of companies from various sectors, including technology, healthcare, financials, energy, and consumer staples. The performance of these individual sectors can significantly impact the overall performance of the S&P 500. For example, if the technology sector is performing well, it can drive the S&P 500 higher, even if other sectors are underperforming.
Identifying the leading and lagging sectors can provide valuable insights for investors. Investors can overweight their portfolios in sectors that are expected to perform well and underweight sectors that are expected to underperform. This strategy is known as sector rotation.
Example: In recent years, the technology sector has been a major driver of the S&P 500's performance. Companies like Amazon, Microsoft, and Google have experienced significant growth, which has contributed to the overall rise of the index.
The Impact of Mega-Cap Stocks
The S&P 500 is a market-capitalization-weighted index, meaning that companies with larger market capitalizations have a greater influence on the index's performance. Mega-cap stocks, such as Apple, Microsoft, and Amazon, have a disproportionately large impact on the S&P 500. If these mega-cap stocks perform well, they can drive the entire index higher, even if smaller companies are struggling.
Example: If Apple's stock price rises by 10%, it will have a greater impact on the S&P 500 than if a smaller company's stock price rises by 10%. This is because Apple's market capitalization is much larger than the smaller company's.
Investor Sentiment: The Emotional Rollercoaster
Fear and Greed: The Twin Drivers of Market Volatility
Investor sentiment, or the overall attitude of investors towards the market, can significantly influence the S&P 500's performance. When investors are feeling optimistic and confident, they are more likely to buy stocks, driving prices higher. This is known as a "bull market." Conversely, when investors are feeling fearful and uncertain, they are more likely to sell stocks, driving prices lower. This is known as a "bear market."
Fear and greed are two of the most powerful emotions that can drive investor sentiment. When investors are feeling greedy, they may become overly optimistic and ignore potential risks. This can lead to asset bubbles and unsustainable market valuations. When investors are feeling fearful, they may overreact to negative news and sell off their holdings indiscriminately. This can lead to market crashes and panic selling.
Example: During the dot-com bubble in the late 1990s, investors were overly optimistic about the prospects of internet companies. This led to sky-high valuations and an eventual market crash when the bubble burst.
News and Events: Shaping Market Perceptions
News and events can have a significant impact on investor sentiment. Positive news, such as strong economic data or positive corporate earnings reports, can boost investor confidence and drive the S&P 500 higher. Negative news, such as weak economic data or negative corporate earnings reports, can erode investor confidence and drive the S&P 500 lower.
Unexpected events, such as geopolitical crises or natural disasters, can also have a significant impact on investor sentiment. These events can create uncertainty and volatility in the market, leading to sharp price swings.
Example: The announcement of a breakthrough in a COVID-19 vaccine in late 2020 boosted investor confidence and led to a significant rally in the S&P 500.
Technical Analysis: Reading the Tea Leaves of the Market
Technical analysis is a method of evaluating securities by analyzing statistics generated by market activity, such as past prices and volume. Technical analysts believe that market prices reflect all available information and that past price patterns can be used to predict future price movements.
Technical analysts use various tools and techniques to identify trends and patterns in the market. These tools include charts, moving averages, and oscillators. Technical analysis can be used to identify potential buying and selling opportunities in the S&P 500.
Example: A technical analyst might use a moving average to identify a trend in the S&P 500. If the S&P 500 is trading above its moving average, it suggests that the market is in an uptrend. If the S&P 500 is trading below its moving average, it suggests that the market is in a downtrend.
Navigating the S&P 500: Strategies for Investors
Diversification: Spreading the Risk
Diversification is a key strategy for managing risk in the stock market. By diversifying your portfolio across different asset classes, sectors, and geographic regions, you can reduce the impact of any single investment on your overall returns.
Diversification can be achieved by investing in a variety of stocks, bonds, and other assets. You can also invest in exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the S&P 500 or other broad market indexes. These ETFs provide instant diversification across a large number of companies.
Example: Instead of investing all of your money in a single stock, you can diversify your portfolio by investing in a mix of stocks, bonds, and real estate. You can also invest in an S&P 500 ETF, which will give you exposure to the 500 largest companies in the United States.
Long-Term Investing: Riding Out the Storms
Long-term investing is a strategy that involves holding investments for an extended period, typically several years or even decades. This strategy is based on the belief that the stock market will rise over the long term, despite short-term fluctuations.
Long-term investors are less concerned about short-term market volatility and are more focused on the long-term growth potential of their investments. They are willing to ride out the storms and avoid making rash decisions based on fear or greed.
Example: Instead of trying to time the market by buying and selling stocks frequently, you can adopt a long-term investing strategy by investing in a diversified portfolio and holding it for the long haul. This will allow you to benefit from the long-term growth of the stock market.
Staying Informed: Keeping an Eye on the Market
Staying informed about the market is crucial for making informed investment decisions. This involves keeping up with economic news, corporate earnings reports, and geopolitical events. You can also follow the advice of financial analysts and experts.
However, it's important to be selective about the information you consume. Not all sources of information are created equal. Some sources may be biased or unreliable. It's important to do your own research and make your own decisions.
Example: You can stay informed about the market by reading financial news websites, watching business news channels, and following financial analysts on social media. However, it's important to be critical of the information you consume and to make your own decisions based on your own research.
FAQ: Decoding the S&P 500 Deep Dive
Understanding the Basics
What exactly is the S&P 500?
The S&P 500, or Standard & Poor's 500, is a stock market index that tracks the performance of 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. It's widely regarded as one of the best single gauges of large-cap U.S. equities and a key indicator of the overall health of the stock market. Think of it as a snapshot of how the biggest players in the US economy are doing.
How is the S&P 500 calculated?
The S&P 500 is a market-capitalization-weighted index. This means that the weight of each company in the index is proportional to its market capitalization (the total value of its outstanding shares). Companies with larger market caps have a greater influence on the index's performance. It’s like giving more weight to the bigger kids in a tug-of-war!
How often does the composition of the S&P 500 change?
The composition of the S&P 500 is reviewed and rebalanced periodically by a committee at S&P Dow Jones Indices. Companies can be added or removed based on factors such as market capitalization, liquidity, and sector representation. These changes typically happen quarterly but can occur more frequently in response to mergers, acquisitions, or bankruptcies.
Factors Influencing the S&P 500
How do interest rates affect the S&P 500?
As mentioned earlier, interest rates set by the Federal Reserve have a significant impact. Higher interest rates can make borrowing more expensive for companies, potentially slowing down growth and impacting earnings. Lower interest rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting corporate earnings and the S&P 500. It's a delicate balancing act.
What role does inflation play in the S&P 500's performance?
High inflation erodes purchasing power and can force the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates to combat it. This can create a challenging environment for the stock market, as higher rates can dampen economic growth and corporate earnings. Investors often see inflation data as a key signpost for future market direction.
How do geopolitical events influence the S&P 500?
Geopolitical events, such as wars, political instability, and trade disputes, can create uncertainty and volatility in the market. These events can disrupt supply chains, impact global trade, and lead to sudden sell-offs as investors become risk-averse. Think of it like a sudden earthquake – it can shake things up unexpectedly!
Investing in the S&P 500
What are the best ways to invest in the S&P 500?
The most common way to invest in the S&P 500 is through exchange-traded funds (ETFs) that track the index. These ETFs provide instant diversification across the 500 companies in the index. You can also invest in index mutual funds that track the S&P 500.
Is it a good idea to try to time the market when investing in the S&P 500?
Trying to time the market (buying low and selling high) is extremely difficult, even for professional investors. Most experts recommend a long-term investing approach, focusing on consistent contributions and riding out the ups and downs of the market. Time in the market is often more important than timing the market.
What are some common mistakes investors make when investing in the S&P 500?
Some common mistakes include trying to time the market, overreacting to short-term market fluctuations, and not diversifying your portfolio. It's important to have a long-term investment strategy and to stick to it, even during periods of market volatility. Don't let emotions drive your decisions!
Decoding the S&P 500: Advanced Insights
What are some advanced metrics to watch when analyzing the S&P 500?
Beyond the basic economic indicators, consider looking at metrics like the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, the dividend yield, and the volatility index (VIX). These can offer additional insights into market valuations and investor sentiment.
How do sector rotations affect the S&P 500's performance?
Sector rotation refers to the shifting of investments from one sector of the economy to another in response to changing economic conditions. Identifying these trends can help you understand which sectors are driving the S&P 500's performance and adjust your portfolio accordingly.
What is the "January Effect" and does it still hold true?
The "January Effect" is a historical anomaly where stock prices, particularly small-cap stocks, tend to rise in January. While this effect has weakened over time, it's still worth being aware of, as it can sometimes influence market sentiment at the beginning of the year.
Final Thoughts
Decoding the S&P 500: Key Factors Driving Its Recent Performance is a complex undertaking that requires a solid understanding of macroeconomic trends, corporate earnings, and investor sentiment. By carefully analyzing these factors, investors can gain a better understanding of the forces shaping the market and make more informed investment decisions. While predicting the future is impossible, understanding the past and present can certainly help you navigate the ever-changing landscape of the stock market and achieve your financial goals. So, keep learning, stay informed, and remember that long-term investing and diversification are your best friends!
